Situación de higiene de manos en el personal de blanco Servicio de Urología. Hospital de Clínicas. Paraguay-2023
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18004/anales/2024.057.02.40Palabras clave:
lavado de manos, microrganismos patógenos, prácticas correctasResumen
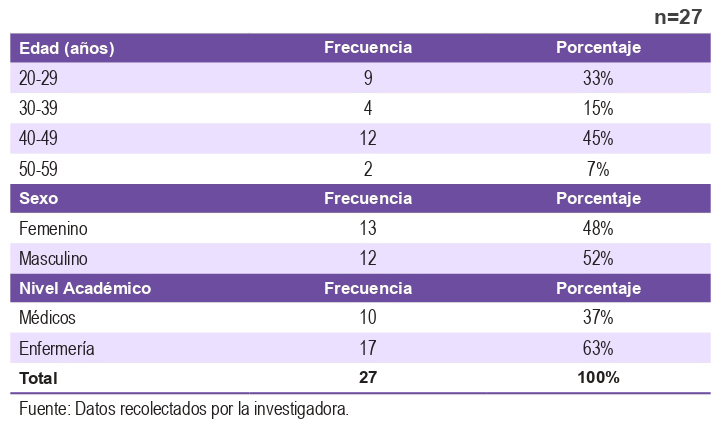
El lavado de manos de los trabajadores de la salud es esencial para prevenir Infecciones Asociadas a la Atención de la Salud. La falta de cumplimiento con esta práctica correcta favorece a la propagación de Microorganismos patógenos. El objetivo fue identificar la situación de Higiene de manos del profesional de la salud del servicio de Urología. Hospital de Clínicas 2023. El estudio fue observacional, correlacional, se llevó a cabo en Hospital de Clínicas. La población de estudio fue de 27 personales de salud. En cuanto a los datos sociodemográficos el 52% son hombres y mujeres 48%. La edad promedio se sitúa predominantemente en los
rangos de 20 a 29 años 33% y 45% de 40-49 años. En lo que respecta a la presencia de bacterias comunes en las manos del profesional de la salud, se identificó principalmente la presencia del 54% de Staphylococcus spp., mientras que Pseudomonas se encontró en cantidades mínimas 4% y que no desarrollaron Bacterias a los 6 días de incubación un promedio de 42%. En cuanto a la resistencia a los antibióticos por parte del profesional de la salud el 28% corresponde a Eritromicina el 24% Clindamicina, el 17% Oxacilina el 9% a Rifampicina el 7% Trimeroprima+Sulfametazol y con 5% los siguientes: Ciprofloxacina, Tetraciclina, Gentamicina,
la gran mayoría con resistencia a Microorganismos Gram (+) como *Staphylococcus aureus. El profesional de la salud demuestra un desempeño aceptable en la prevención de la presencia bacteriana, aunque aún existe margen de mejora, se recomienda revisar y fortalecer prácticas para prevenir la presencia bacteriana.