Impacto económico de desbridamientos quirúrgicos y amputaciones de miembros inferiores en pacientes diabéticos
Palabras clave:
diabetes, desbridamientos, amputaciones, costoResumen
Introducción: La diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2) constituye un problema de salud pública.
Objetivos: Determinar la frecuencia de los desbridamientos quirúrgicos y amputaciones de
miembros inferiores en pacientes diabéticos tipo 2 y su impacto económico. Materiales y
métodos: Se realizó un estudio Observacional descriptivo de corte transversal. Se estimaron
los costos médicos directos tanto de desbridamientos quirúrgicos como de amputaciones
de miembros inferiores en pacientes diabéticos en el Hospital de Clínicas San Lorenzo,
durante el año 2019. Resultados: El total de desbridamientos quirúrgicos y amputaciones de
miembros inferiores en el año 2019 representan el 1,9% (314/16.484) de los procedimientos
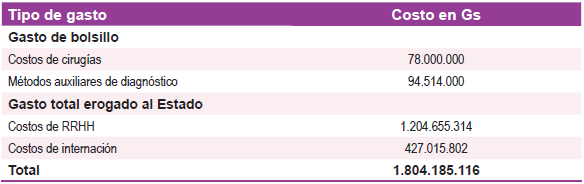
quirúrgicos realizados en el Hospital de Clínicas. El monto total de gastos es de 1.804.185.116
(262.541 USD), de los cuales 172.514.000 (38.857 USD) constituyen gastos de bolsillo y
1.631.671.116 (237.437 USD) constituyen gastos erogados al Estado Paraguayo a través del
Hospital de Clínicas de San Lorenzo. Conclusión: Las complicaciones de la diabetes imponen
considerables costos tanto en el gasto de bolsillo, al sector de la salud como a la economía
en general en el Paraguay, por lo que es necesario re evaluar el manejo de esta problemática
teniendo en cuenta el gran impacto que tienen dichos procedimientos producen en la vida
de los pacientes a nivel físico, emocional, familiar y social, así como la carga económica que
conlleva el tratamiento para el Sistema de Salud.
Referencias
Oggiam, D. S. (2021, 10 febrero). Neuropathic pain screening for diabetes mellitus: a conceptual analysis. SCIELO BRASIL. Recuperado 28 de febrero de 2022, de https://www.scielo.br/j/brjp/a/WWNgJMgHDsswhpKT7hbMRdm/?format=html.
Kautzky-Willer, A., Harreiter, J., & Pacini, G. (2016). Sex and Gender Differences in Risk, Pathophysiology and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrine reviews, 37(3), 278–316. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2015-1137.
Font-Jimenez, I. (2016, 1 marzo). Factores psicosociales implicados en la amputación. Revisión sistemática de la literatura | Atención Primaria. ELSEVIER. Recuperado 28 de febrero de 2022, de https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-atencion-primaria-27-articulo-factores-psicosociales-implicados-amputacion-revision-S0212656715002097.
Alvarsson, A., Sandgren, B., Wendel, C., Alvarsson, M., & Brismar, K. (2012). A retrospective analysis of amputation rates in diabetic patients: can lower extremity amputations be further prevented?. Cardiovascular diabetology, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-11-18.
Chaparro Cubilla A, Rodriguez Candia E. Amputación de miembro inferior en pacientes diabéticos del Hospital de Clínicas de Asunción – Paraguay. Una estimación de costos directos. An Univ Nac Asuncion [Internet]. 2015 [citado el 17 de agosto de 2023];44(2):23–34. Disponible en: http://archivo.bc.una.py/index.php/RP/article/view/190/123.
Mendoza Romo, M. Á., Padrón Salas, A., Cossío Torres, P. E., & Soria Orozco, M. (2017). Prevalencia mundial de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y su relación con el índice de desarrollo humano. Revista panamericana de salud pública = Revista panamericana de salud pública, 41, e103. https://doi.org/10.26633/RPSP.2017.103.
Costo del tratamiento de un diabético asciende a más de G. 3 millones al año [Internet]. Gov.py. 2015 [citado el 17 de agosto de 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.mspbs.gov.py/portal/6102/costo-del-tratamiento-de-un-diabetico-asciende-a-mas-de-g-3-millones-al-ano.html.
Xu, Z., Yu, D., Yin, X., Zheng, F., & Li, H. (2017). El estatus socioeconómico se asocia con la prevalencia mundial de la diabetes. Oncotarget, 8(27), 44434–44439. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17902.
Ng, J., Clement, I. J., Jimeno, C., Sy, R. A., Mirasol, R., De La Pena, P., Panelo, A., Tan, R., Santillán, M., Bayani, D., & Wiebols, E. (2020). Estimación de los costos médicos directos de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en Filipinas: un protocolo. BMJ abierto, 10(7), e025696. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025696.
Erzse, A., Stacey, N., Chola, L., Tugendhaft, A., Freeman, M., & Hofman, K. (2019). The direct medical cost of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Africa: a cost of illness study. Global health action, 12(1), 1636611. https://doi.org/10.1080/16549716.2019.1636611.